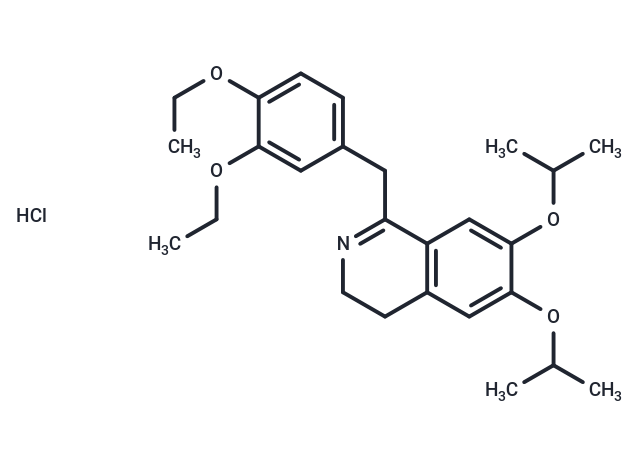
Diproteverine HCl
CAS No. 69373-88-2
Diproteverine HCl( —— )
Catalog No. M36266 CAS No. 69373-88-2
Diproteverine HCl is a novel calcium antagonist with antianginal properties, antispasmodic and vasoactive.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 2MG | 296 | Get Quote |


|
| 5MG | 409 | Get Quote |


|
| 10MG | 604 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 908 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 1251 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 1647 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 3312 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameDiproteverine HCl
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionDiproteverine HCl is a novel calcium antagonist with antianginal properties, antispasmodic and vasoactive.
-
DescriptionDiproteverine HCl is a novel calcium antagonist with antianginal properties, antispasmodic and vasoactive.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayGPCR/G Protein
-
TargetCalcium Channel
-
RecptorCalcium Channel
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number69373-88-2
-
Formula Weight462.02
-
Molecular FormulaC26H36ClNO4
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
Solubility——
-
SMILESCl.N1=C(C=2C=C(OC(C)C)C(OC(C)C)=CC2CC1)CC3=CC=C(OCC)C(OCC)=C3
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
molnova catalog



related products
-
Isradipine
Isradipine is a potent and selective L-type voltage-gated calcium channel blocker, used to treat high blood pressure.
-
CALP3
Cell-permeable calmodulin (CaM) agonist that binds to the EF-hand/Ca2+-binding site. Activates phosphodiesterase in the absence of Ca2+ and inhibits Ca2+-mediated cytotoxicity and apoptosis (IC50 = 33 μM).
-
A-1048400
A novel potent, selective, orally active N-type and T-type calcium channel blocker with IC50 of 1.4 and 1.2 uM, respectively.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


